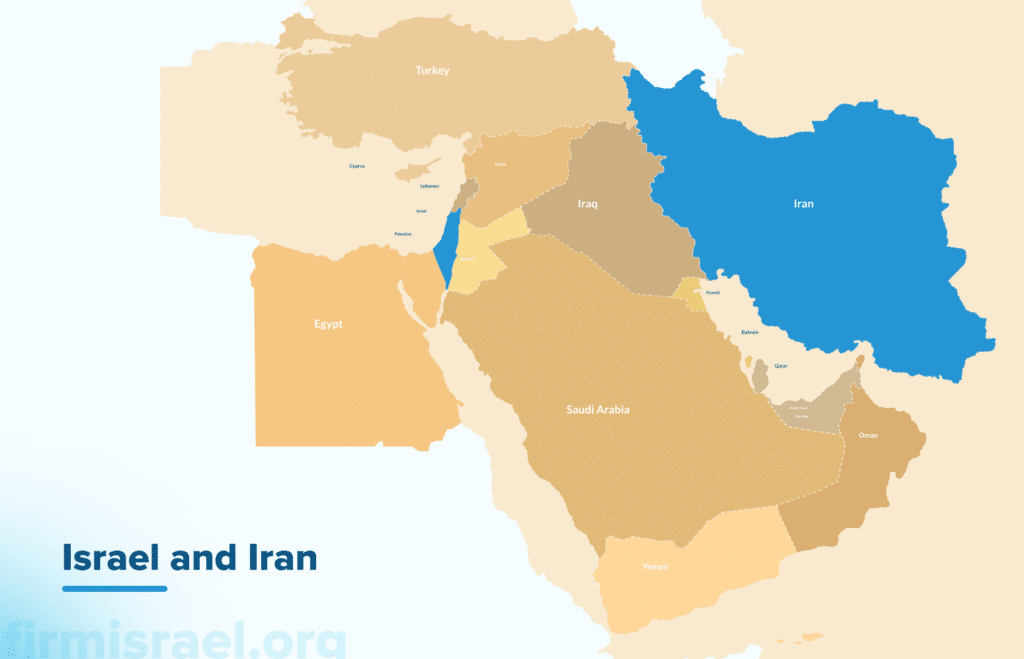
Iran and Israel
Saturday night, April 13, Iran launched an attack on Israel. Although such a direct attack was unexpected, Iranian hostility towards Israel is not new. The leaders of the Jewish state have been warning the world against Iran for years. But why?
Both the history of Iran and the modern developments in Israel relations with Iran are as complex as they are significant. One could argue that it has been so since biblical times. So, what is there to know about both recent and ancient history of Iran and Israel?
Let’s piece some of these puzzles together, starting with the most recent.
Iran Attacks Israel on April 13
Iran fired over 300 missiles and drones towards Israel on April 13. At around 2 AM, swarms of rockets appeared in the sky all over Israel, but also over Jordan and the surrounding region.
The Israeli military, together with the United States, the UK, and even forces from Jordan, Saudi Arabia and UAE helped shoot down 99% of the missiles. Miraculously, not a single person was killed.
Iran has never in its modern history attacked Israel directly. The Islamic Regime tends to operate through proxies, which are terrorist organizations they fund in the Middle East.
The ostensible reason for this attack was the alleged Israeli strike against IRGC headquarters (located right beside the Iranian Embassy in Syria). Nevertheless, Iran’s response is a major escalation, as their missiles were aimed at Israel’s sovereign territory.
Saturday night, Iran showed the world their true face and clear intentions. They are committed to Israel’s destruction, which they have been openly talking about for years. But now, they are acting on it, too.
Since some Muslim countries in the Middle East took a public stand with Israel in recent days, it appears that the Islamic Republic of Iran is willing to start a regional war.
What’s the Difference between Iran and the Islamic Republic?
The term “Iran” refers to the country located in the Middle East. Meanwhile the “Islamic Republic” (often also called the Islamic Regime) typically refers to the government and political system that has been in place in Iran since the Iranian Revolution of 1979.
Iran has a rich cultural heritage and has been an influential center of civilization in the region. It is very diverse ethnically to this day, and even included a significant Jewish population. That is, until the revolution.
The Islamic regime was established after overthrowing the monarchy of Iran in 1979. The goal of the revolution was to overthrow the autocratic rule of the Shah. It was a broad-based movement, but ultimately, the Shah fell under the dominance of the Islamic revolutionaries.
The Islamic Republic in Iran grants ultimate authority to the Supreme Leader, a religious cleric. He serves as the highest-ranking political and religious authority in the country. The Supreme Leader, in turn, oversees various government institutions, including judicial offices and the military apparatus.
Under the rule of the Shah, Iran and Israel maintained diplomatic relations and cooperation in various fields, including intelligence. However, after the Iranian Revolution, the Islamic regime severed these ties and adopted an openly hostile stance toward Israel.
Nevertheless, the same attitude cannot be ascribed to the broader Iranian society. There have been protests in Iran against the government’s policies, and the people have protested even the government stance toward Israel.
The Links Between Iran and the Enemies of Israel
As previously mentioned, the Islamic Republic of Iran often operates through their proxies in the region. These include terrorist organizations and militias like Hezbollah in Lebanon, Hamas in Gaza, or the Houthis in Yemen (and more).
Hezbollah is perhaps the most well-known and most powerful Iranian proxy, and they are part of the same Shia sect as Iran. Based in Lebanon, it was formed during the Lebanese Civil War in the 1980s. Hezbollah receives significant financial, military, and logistical support from Tehran. And unsurprisingly, they are considered a significant threat to Israel’s security.
Hamas, though usually associated specifically with Gaza, is active in all Palestinian Territories. Hamas has historical ties to the Sunni Muslim Brotherhood, but it has received significant support from Iran, also in the form of weapons and training. Iranian intelligence continues to play a key role in the ongoing war between Israel and Hamas today.
The Houthi Rebels in Yemen have been engaged in a long-running conflict with the Yemeni government and a Saudi-led coalition since 2015. Evidence suggests that Iran provided military assistance to the group (but has little direct control over their operations). Though primarily focused on their domestic conflict, the Houthis have expressed anti-Israel rhetoric, made many statements condemning Israel, launching missiles at Israel and Israel-bound ships in the Red Sea.
The conflict in Yemen is widely seen as a proxy war between Iran and Saudi Arabia for regional dominance. Thus, Iran is driven by its desire to not just annihilate Israel, but to also counter its regional rivals.
How Israel-Iran Relations Changed In 1979
In differentiating between the people of Iran and the Islamic Republic, we mentioned the Iranian Revolution of 1979.
Prior to the revolution, Israel and Iran maintained relatively close ties, albeit somewhat unofficially. Nevertheless, Israel was known to even provide military support to Iran under the rule of the Shah.
Under the rule of Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, Iran and Israel maintained covert intelligence and military cooperation. It was driven by shared concerns about Arab nationalism and Soviet influence in the region.
After the revolution, diplomatic relations between the two countries deteriorated significantly. The Islamic regime not only supports anti-Israel militant groups, but has also been pursuing nuclear capabilities, which Israel views as a threat to its security.
It’s important to note that the revolution impacted not just Iran’s relations with Israel, but with the entire Middle East.
For example, prior to 1979, Iran’s relations with Saudi Arabia were generally cordial. Both countries were ruled by monarchies and shared common interests, such as maintaining stability in the region and combating communism. This is no longer the case today.
Why Iran and not Persia?
The name “Iran” and “Persia” refer to the same geographic region, but they have different historical and cultural connotations.
The name “Persia” was derived from the ancient Greek term “Persis,” which referred specifically to the land centered in the province of Fars (or Pars) in southwestern Iran. Over time, the name “Persia” became commonly used in Western languages to refer to the entire region of modern-day Iran.
However, in 1935, the Iranian government officially requested that foreign countries use the name “Iran” instead of “Persia” to refer to the country. And the name “Iran” comes from the word “Aryan”.
(If that word sounds familiar to you, that is probably because it is the name of the race that Hitler considered superior. In an effort to keep the Aryan race “pure”, Hitler tried to wipe out Jews, Slavs, and the Roma people – to begin with – from Europe and the world.)
By adopting the name “Iran,” the government sought to distance itself from the historical associations and stereotypes associated with the name “Persia”. It wanted to present itself as a modern nation with a rich cultural heritage.
Iran in the Bible (Persia) and Israel
Iran surfaces several times in the Bible. The first mention of the Persian region in the Bible appears in the Book of Daniel:
“In the third year of the reign of Jehoiakim king of Judah, Nebuchadnezzar king of Babylon came to Jerusalem and besieged it. And the Lord gave Jehoiakim king of Judah into his hand, with some of the vessels of the house of God. And he brought them to the land of Shinar, to the house of his god, and placed the vessels in the treasury of his god.” (Daniel 1:1-2)
While Persia is not specifically mentioned by name, the reference to the “land of Shinar” corresponds to modern-day Iran, where the Persian Empire later arose. Daniel served in the courts of Babylon and later Persia, providing additional references to the region and its rulers.
Later, the book of Esther tells the story of Queen Esther, a Jewish woman who became a queen of Persia and played a crucial role in saving her people from genocide.
One significant biblical figure associated with Persia is Cyrus the Great. He was in fact the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. Cyrus the Great and Darius the Great conquered Babylon and incorporated it into their empire (along with the Jewish captives who were already in Babylon).
In the book of Ezra, Cyrus is depicted as issuing a decree allowing the Jewish exiles in Babylon to return to Jerusalem and rebuild the Temple. This is seen as a pivotal moment in Jewish history, marking the end of the Babylonian exile.
What Does It All Mean?
As mentioned in the very beginning, the relations between Israel and Iran or Persia are far from simple. The imminent threats to Israel’s security seem to arise at regular intervals – truly since antiquity, but a lot more frequently in the modern age.
At the same time, with every such threat, God raises friends and allies for Israel – even from within enemy territory! Whether it’s other Muslim countries or the Iranian people themselves (as seen especially on social media), Israel appears to have many unexpected friends.
As believers, we remain watchful and pray for God’s protection, guidance, and wisdom. We also want to be mindful of Biblical prophecies and ask the Holy Spirit to reveal God’s plans to His Church and His people Israel.
How Can We Pray?
This is a time for the nations to decide whether to stand with Israel or not.
Pray for the believing body in Israel to use this time of fear to bring a message of hope and of peace in Yeshua. We don’t know what the future holds, but we know who holds our future. Something big is happening, and though it may feel far away (geographically) from your community, it is a major world event that could have global repercussions.
At the same time, we pray for the people of Iran, oppressed by their own government. For one, the people do not want a war with Israel. But what is more, we are hearing of great openness among the Iranians to the Gospel! So, we pray that even in these circumstances the Kingdom of God would advance in the Middle East.
We are asking the Lord for wisdom for our leaders, the government of Israel, and for us, believers in the land. How would God have us respond? No weapon formed against us will prosper, and the Keeper of Israel neither slumbers nor sleeps.

How to Pray for Israel: Free PDF Download
Today, more than ever, Israel needs your prayers. Learn three simple and effective ways to stand with Israel in prayer, today.
We’ve put this guide together for you so that you are even better equipped to bless Israel as you pray for Her.
Articles Related to Iran and Israel: The April 13 Attack, Plus Recent and Biblical History
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes